Thermostats are an essential component of your home’s heating and cooling system. They regulate the temperature in your home, making sure it stays comfortable all year round. While most people are familiar with the basic functions of a thermostat, not everyone is aware of the importance of RC and RH. Understanding these two terms is crucial to making sure your thermostat is functioning properly.
Knowing the basics about thermostat wiring can be quite useful as a homeowner, especially when there are issues with your HVAC system. There may come a time when you don’t have immediate access to a technician, and a little knowledge about your system can help you fixed minor issues. Understanding how these terminal letters on a Thermostat can also help you communicate more effectively with an HVAC professional when a repair is needed.
RC and RH: How Do They Work?
In most HVAC systems, the thermostat is powered by heating and cooling systems. The RH wire controls the heating system, while the RC wire powers the cooling system. Both are designed to work together to maintain the desired temperature in your home. When the temperature rises, the cooling system activates through the RC wire, and when it falls, the heating system activates via the RH wire.
In a modern HVAC system, there may be only one transformer supplying power for both heating and cooling. In this case, the RC and RH terminals might be connected by a jumper wire, meaning one wire controls both functions.
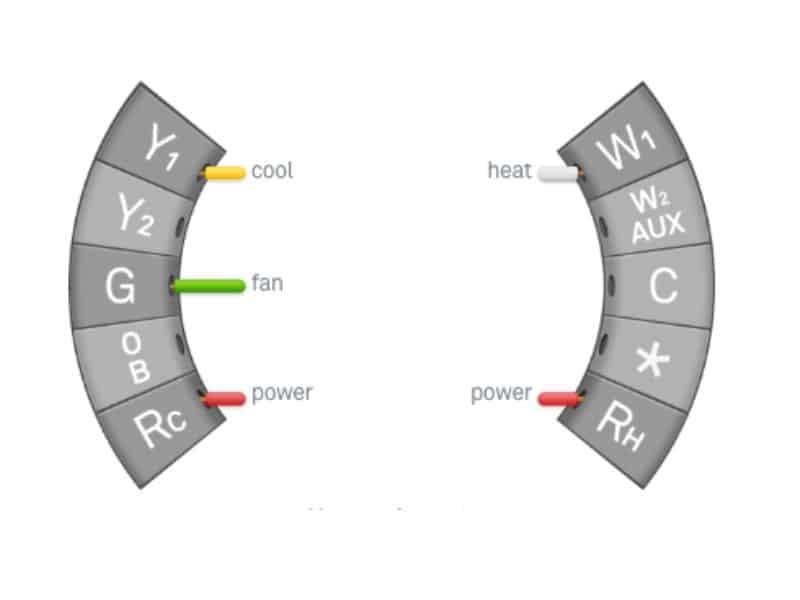
What is RC on a Thermostat?
RC (which stands for “cooling relay”) is the 24-volt cooling power supply terminal on a thermostat. It is used to connect the thermostat to the air conditioning system’s power source.
In a four-wire heat/cool system and a single-stage heat pump system, the RC and RH terminals are jumpered together to allow the thermostat to control both heating and cooling systems. However, in a five-wire heating/cooling system, the RC and RH terminals are not jumpered.
What is RH on a Thermostat?
RH (which stands for “heating relay”) is the 24-volt heating power supply terminal on a thermostat. It is used to connect the thermostat to the heating system’s power source.
In a four-wire heat/cool system and a single-stage heat pump system, the RH and RC terminals are jumpered together. However, in a five-wire heating/cooling system, the RH and RC terminals are not jumpered.
Differences between RC and RH Terminal
RC: Powers the cooling system.
RH: Powers the heating system.
The RC (Cooling) and RH (Heating) terminals on a thermostat serve different functions, even though they are both related to powering the thermostat.
RH Terminal (Red Heating): This terminal is designated for the heating system and connects to the transformer that powers the furnace. It supplies the voltage to run your heating system.
RC Terminal (Red Cooling): This terminal controls the power for the air conditioning system. It connects to the transformer responsible for cooling (AC). In HVAC systems, the RC terminal delivers the voltage needed for the cooling components of your HVAC system to work.
How to Use RC and RH on a Thermostat
Using RC and RH on your thermostat is straightforward, but there are a few things you need to know to get the most out of these features.
Common Configurations:
- Single Transformer Systems: In most modern HVAC systems, a single transformer powers both heating and cooling systems. In these setups, there is often a jumper wire connecting RC and RH, meaning only one transformer powers both systems.
- Dual Transformer Systems: In some older or specialized HVAC systems, separate transformers power the heating and cooling components. In this case, the RC and RH terminals are separate and connected to their respective systems.
Make sure you have a clear understanding of the desired temperature and humidity levels in your home. This information will help you to set your thermostat correctly, ensuring that it is functioning optimally.
To set your thermostat, simply follow the manufacturer’s instructions for adjusting the temperature and humidity settings.
Once you have set the temperature and humidity levels, the RC and RH features on your thermostat will work automatically to maintain these levels in your home. You may need to adjust the settings periodically, especially during seasonal changes, to ensure that your thermostat is functioning correctly.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using RC and RH on a Thermostat
While using RC and RH on your thermostat is straightforward, there are a few common mistakes you should avoid.
First, make sure that you have the correct type of thermostat for your heating and cooling system. Some thermostats are designed specifically for use with certain types of systems, and using the wrong thermostat can result in problems with performance and accuracy.
Another common mistake is not maintaining your thermostat correctly. Regular cleaning and maintenance of your thermostat can help to ensure that it is functioning correctly and that the RC and RH features are working optimally.
Finally, avoid making large adjustments to your thermostat’s temperature and humidity settings. Small adjustments are better, as they are less likely to cause problems with performance and accuracy.
Conclusion
RC and RH are two important terms in thermostat wiring and operation. Understanding what they mean and how they are used can help homeowners troubleshoot any issues with their thermostats and ensure it’s functioning properly.
RC stands for “power” or “24Vac common” and refers to the low-voltage power supply that powers the thermostat. RH stands for “heat” and is used to control the heating system in a home. Knowing the difference between these two terms and how they work in a thermostat can be crucial for fixing problems and maintaining a comfortable and efficient heating system.






