Knowing whether your furnace is powered by gas or electricity is essential for maintenance, troubleshooting, and even understanding your energy bills. While it might seem obvious to some, it’s not always immediately clear. This friendly guide will walk you through the simple steps to quickly and easily identify your furnace type.
Identifying your furnace type is important for several reasons:
- Troubleshooting: Different furnace types have different potential problems. Knowing whether you have a gas or electric furnace helps you narrow down the possible causes of any issues.
- Maintenance: Gas furnaces require different maintenance than electric furnaces. For example, gas furnaces require regular checks of the gas connections and venting system, while electric furnaces do not.
- Energy Bills: Gas and electricity are billed differently, and knowing your furnace type helps you understand your energy consumption and costs.
- Safety: Understanding your furnace type is crucial for safety, especially with gas furnaces, which can pose a risk of carbon monoxide poisoning if not properly maintained.
Simple Ways to Identify Your Furnace Type
Here are some easy ways to determine if your furnace is gas or electric:
1. Check for a Gas Meter
The most obvious indicator is the presence of a gas meter outside your home. If you have a gas meter, it’s highly likely that you have gas appliances, including a gas furnace.
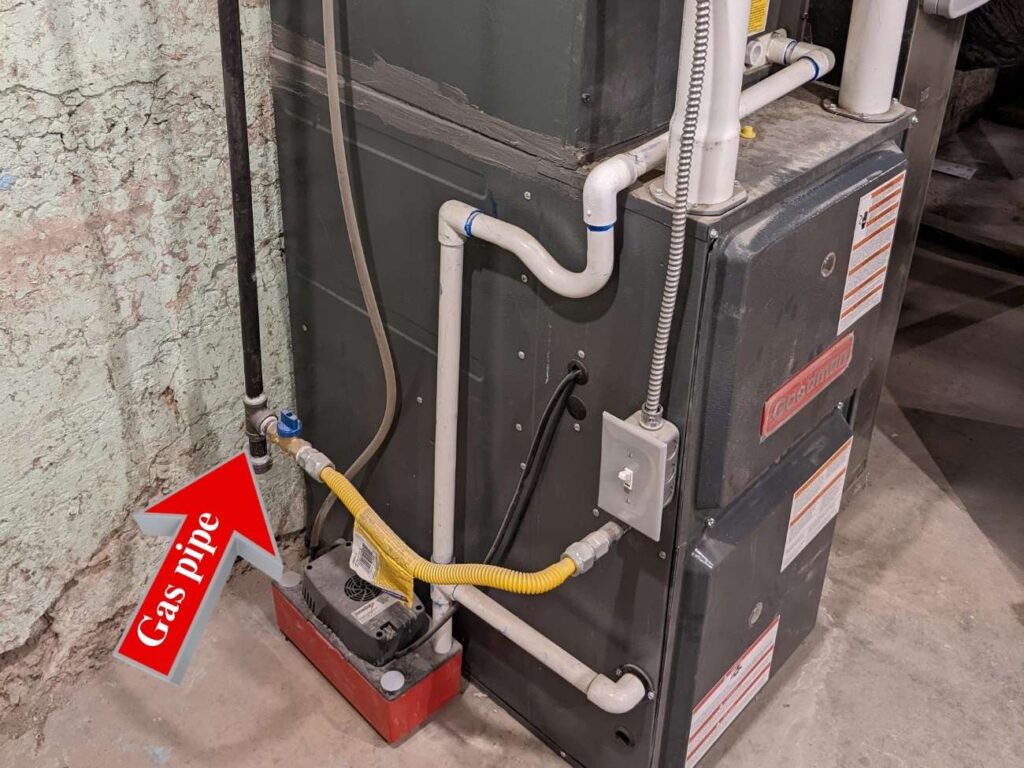
2. Look for Gas Pipes
Look for gas pipes entering your furnace. These are usually black iron pipes. If you see gas pipes connected to your furnace, it’s a gas furnace.

3. Check for a Chimney or Vent
Gas furnaces require venting to expel combustion byproducts. Look for a chimney, vent pipe (usually metal), or a direct vent system that goes through the side of your house. Electric furnaces do not require venting.
4. Listen for Ignition
When your furnace starts, listen carefully.
- Gas Furnace: You’ll typically hear a clicking sound (from the igniter) followed by a whooshing sound as the gas burners ignite.
- Electric Furnace: You’ll usually hear a humming sound as the heating elements turn on. There won’t be any clicking or whooshing sounds associated with combustion.
5. Check the Breaker Box
Look at the breakers in your electrical panel.
- High-Amp Breaker: If you see a double-pole breaker (takes up two slots) with a high amperage rating (e.g., 30, 40, 50 amps) dedicated to the furnace, it’s likely an electric furnace. Electric furnaces require a significant amount of electricity.
- No High-Amp Breaker: If there’s no unusually high amperage breaker dedicated to the furnace, it’s more likely a gas furnace (which uses only a small amount of electricity for the blower motor and controls).
6. Check the Furnace Label or Nameplate
Look for a label or nameplate on the furnace itself. It usually contains information about the furnace type, fuel source, and other specifications. Look for terms like “natural gas,” “propane,” or “electric.”
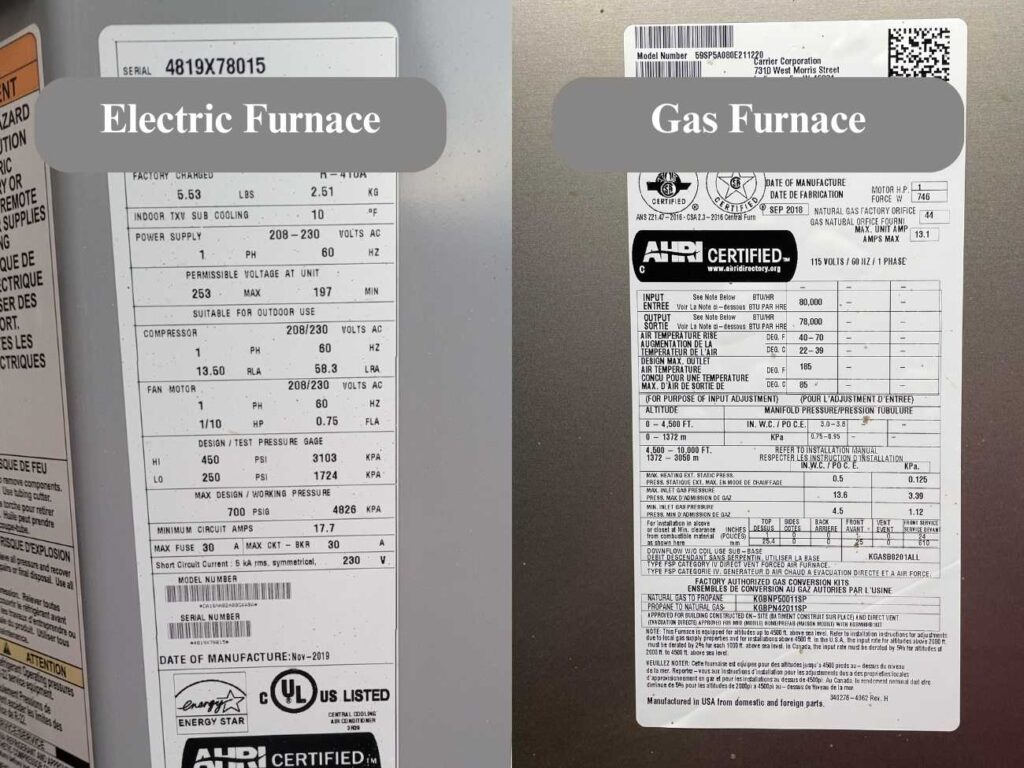
7. Check Your Energy Bills
Your energy bills will clearly show whether you’re being billed for natural gas or just electricity. If you receive a gas bill, you likely have a gas furnace.
Visual Differences (Quick Summary):
- Gas Furnace:
- Gas pipes connected to the unit.
- Chimney, vent pipe, or direct vent.
- Clicking and whooshing sounds during ignition.
- No unusually high-amp breakers dedicated to the furnace.
- Electric Furnace:
- No gas pipes.
- No chimney or vent (unless it’s a heat pump system, which is different).
- Humming sound during operation.
- High-amp double-pole breaker dedicated to the furnace.
Gas vs Electric Furnace Comparison
| Feature | Gas Furnace | Electric Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Natural gas or propane | Electricity |
| Upfront Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Operating Cost | Lower (depends on gas prices) | Higher (depends on electricity rates) |
| Efficiency | 80-97% AFUE (less efficient than electric) | 100% efficiency (all energy converts to heat) |
| Lifespan | 15-20 years | 20-30 years |
| Maintenance | Requires regular cleaning and checks for gas lines | Minimal maintenance required |
| Environmental Impact | Produces emissions, less eco-friendly | Eco-friendly if using renewable electricity |
| Heating Speed | Heats up quickly | Slower to heat up |
| Installation Complexity | More complex due to gas lines | Easier to install |
| Best For | Cold climates with access to natural gas | Milder climates or homes without gas access |
What if I Have a Heat Pump?
Heat pumps are a type of electric heating and cooling system that can sometimes be mistaken for gas furnaces. They don’t use combustion to generate heat; instead, they transfer heat from the outside air (even in cold temperatures) to the inside of your home.
If you have a heat pump, you won’t see gas pipes or a chimney/vent in the same way you would with a gas furnace. However, you will likely see a large outdoor unit (similar to an air conditioner condenser).
If you’re still unsure about your furnace type after checking all these clues, it’s best to consult a qualified HVAC technician. They can quickly and accurately identify your furnace type and provide any necessary maintenance or repairs.
Knowing whether your furnace is gas or electric is a simple but important piece of homeownership knowledge. By following these easy steps, you can confidently identify your furnace type and be better prepared for maintenance, troubleshooting, and understanding your energy consumption.






