Understanding the error codes of a Heil high-efficiency furnace is essential for maintaining optimal performance and longevity. Heil furnaces, known for their reliable manufacturing and superior home comfort, may occasionally display error codes on their control board through a flashing LED sequence or a digital display. This guide aims to demystify these codes, offering insights into common issues, troubleshooting tips, and maintenance advice for your Heil furnace.
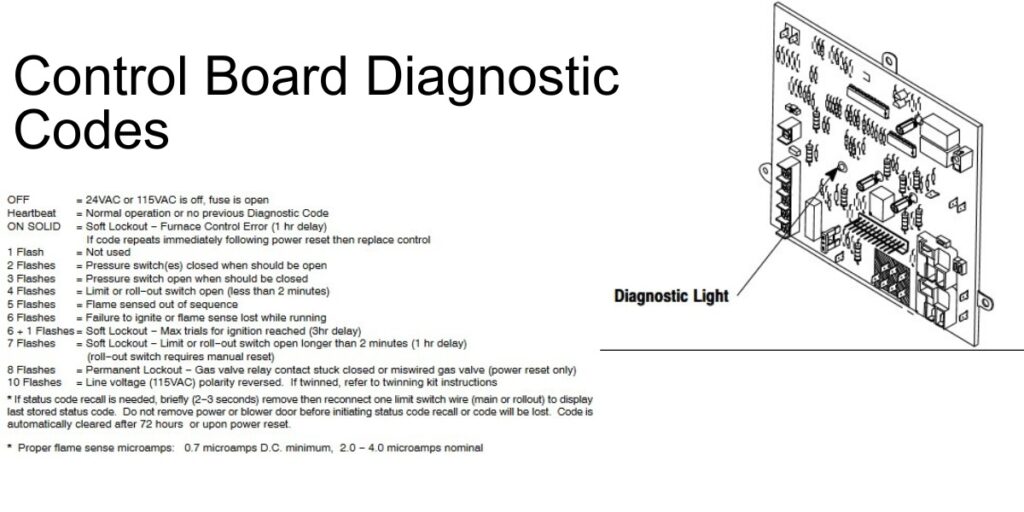
The following section is designed to provide homeowners and technicians with a clear understanding of each error code. By accurately interpreting these Heil furnace codes, you can gain insights into potential issues and take appropriate action to maintain or restore your furnace’s optimal performance.
Decoding Common Heil Furnace Error Codes
Whether troubleshooting a problem or conducting routine checks, this guide will be invaluable in your home maintenance toolkit.
LED Off
Meaning: This code indicates an open secondary voltage fuse, suggesting an issue with the furnace’s internal power supply.
Action: Check the door switch to ensure it’s not open. Verify the voltage at L1 and the neutral point. Inspect the 24 V fuse and the 24VAC RED and COM Blue connections for any signs of short circuits.
LED On
Meaning: This signifies a control circuitry lockout in your furnace.
Action: The system will automatically reset after an hour. In the meantime, check for any system errors or issues that might have triggered this lockout.
LED Solid
Meaning: This code points to a gas valve relay being stuck open, a significant concern for furnace operation.
Action: Conduct a software check for errors and inspect the flame sensor circuit. If the problem persists, reset the power to clear the lockout or consider replacing the control if the code reappears.
LED Flashing Like a Heartbeat
Meaning: This pattern indicates that the control has 24 VAC power, showing that the basic power supply to the furnace is functioning correctly.
Action: No immediate action is required unless other error codes or operational issues exist.
2 Flashes
Meaning: The system indicates that the pressure switch did not open, a potential airflow issue.
Action: Look for blocked pressure tubing or any obstructions affecting the pressure switch’s operation.
3 Flashes
Meaning: This code is activated when the pressure switch fails to close or opens again, pointing to ventilation issues.
Action: Check for wrong vent size, excessive wind, inducer motor issues, or a faulty pressure switch. Also, inspect the pressure tubing for disconnections or blockages and verify the combustion air supply.
4 Flashes
Meaning: Indicates a limit circuit fault, such as a flame rollout or an open limit, which are serious safety concerns.
Action: Check for a loose blower wheel, blocked vent, correct vent sizing, dirty filter, or a defective blower motor. Ensure that all connections and switches are functioning properly.
5 Flashes
Meaning: This signals an irregular flame proving signal, which means the flame is not detected consistently.
Action: Verify if the gas valve is stuck open or leaking. Inspect the flame sensor and the entire ignition process for any anomalies.
6 Flashes
Meaning: Indicates that the furnace is not igniting or the flame sense is lost during operation.
Action: Ensure that the flame sensor is not grounded and free of oxide buildup. Check for low inlet gas pressure, a faulty hot surface ignitor, and proper flame sense microamps. Also, verify the condition and operation of the gas valve.
7 Flashes
Meaning: A limited circuit lockout has occurred. This happens when the limit/flame rollout stays open for over 3 minutes.
Action: The control will auto-reset after three hours. Inspect the limit switch and flame rollout sensor for issues during this time.
8 Flashes
Meaning: Indicates a lockout due to gas heating issues.
Action: The auto-reset will not occur in this case. Check the control valve for faults and verify that the gas valve is not miswired.
10 Flashes
Meaning: This code indicates reversed polarity within the system, which can affect the furnace’s operation.
Action: If your setup includes twinned furnaces, check the twinning kit and ensure all connections adhere to the manufacturer’s specifications.
1 Flash, then 2 Flashes
Meaning: This sequence indicates that the blower is on after power-up, a normal operation during a heat request.
Action: No action is needed if this sequence appears during a normal operation cycle.
6 Flashes, then 1 Flash
Meaning: This code represents an ignition lockout, a significant issue affecting the furnace’s starting ability.
Action: The system will automatically reset after three hours. In the meantime, inspect the ignition system for any potential lockout causes.
Advanced Troubleshooting for Common Heil Furnace Issues
The efficient operation of a Heil furnace is essential for maintaining a comfortable and warm environment in your home. However, like all complex systems, furnaces can experience various issues that affect their performance. Understanding how to identify and troubleshoot common problems is key to ensuring your furnace runs smoothly and efficiently.
Here is a range of typical problems homeowners may encounter with their Heil furnaces.
Furnace Not Heating
When your Heil furnace fails to produce heat, the cause can range from simple electrical issues to more complex component failures.
Troubleshooting: First, check for any electrical shorts or blown fuses associated with the furnace. Reset the associated circuit breaker if necessary. Next, inspect the furnace igniter for cracks or defects. If cracked, replace the igniter. If it appears intact, use a multimeter to test for continuity. If the igniter is not the issue, further investigation may be required into the gas supply and burner operation.
Furnace Cycling Irregularly
If the furnace turns on and off more frequently than normal, it may be due to incorrect thermostat settings or internal component malfunctions.
Troubleshooting: Begin by checking the thermostat. If it has an adjustable calibration scale, adjust the heat anticipator. If this doesn’t resolve the issue, or if your thermostat lacks such a feature, consider replacing the thermostat. Additionally, inspect the furnace’s flame sensor and other safety circuits, as these can cause frequent cycling if malfunctioning.
Furnace Not Blowing Hot Air
A furnace blowing cold air or not blowing air at all can indicate issues with the blower motor or related components.
Troubleshooting: Check if power is reaching the blower motor. If power is present, but the motor doesn’t run, the motor might be burned out and need replacement. If the motor runs, but no air is moving, the issue could be a broken connecting belt. Replace the belt if necessary. Additionally, inspect the control board as a faulty relay can cause continuous voltage supply to the motor, preventing proper operation.
Blower Motor Issues
The blower motor is critical in circulating warm air through your home. Issues with this component can significantly affect your furnace’s performance.
Troubleshooting: Ensure that power is reaching the blower motor. If the motor receives power but does not operate, it may be burned out and require replacement. Check for obstructions or motor damage if the motor hums but the blower fan does not spin freely. In some cases, replacing the blower motor may be necessary.
Furnace Noise or Loud Operation
Noisy furnace operation can be due to loose components, such as the blower wheel, or mechanical wear and tear.
Troubleshooting: Inspect the blower wheel. Ensure that the set screw attaching the wheel to the motor shaft is tight. Also, examine the wheel for any signs of damage. If the blower wheel is damaged or unsafe, replacing it might be necessary to eliminate the noise and ensure efficient operation.
The Furnace Started and Stopping Shortly After
This issue, often called short cycling, can be caused by a faulty flame sensor or other safety devices in the furnace.
Troubleshooting: Check the furnace’s flame sensor. If it is dirty, clean it using a fine abrasive pad. If the sensor appears defective or cleaning it does not solve the issue, consider replacing it. Additionally, inspect other safety components like the high-limit switch, as these can cause the furnace to shut off prematurely if they malfunction.
In conclusion, understanding and effectively responding to Heil furnace error codes is integral to maintaining and troubleshooting your home’s heating system. These error codes, designed to communicate specific issues and operational statuses, are the first defense in ensuring your furnace operates efficiently and safely.
By familiarizing yourself with the meanings behind these codes and the actions required to address them, you can significantly enhance the longevity and performance of your Heil furnace.
Regular maintenance is crucial in ensuring the durability and efficiency of your furnace. A simple yet vital task is regularly changing the air filter. This not only prolongs the life of your unit’s blower motor but also prevents the compressor coils from clogging, ensuring that your furnace operates at its highest efficiency.
However, while many furnace issues can be addressed through basic troubleshooting, more complex problems may require professional expertise. In such cases, it’s important to consult a certified HVAC technician. Their specialized knowledge ensures that your furnace not only operates efficiently but also maintains the comfort and safety of your home. With this Heil furnace codes, you are better prepared to keep your home heating system functioning optimally throughout the year.






